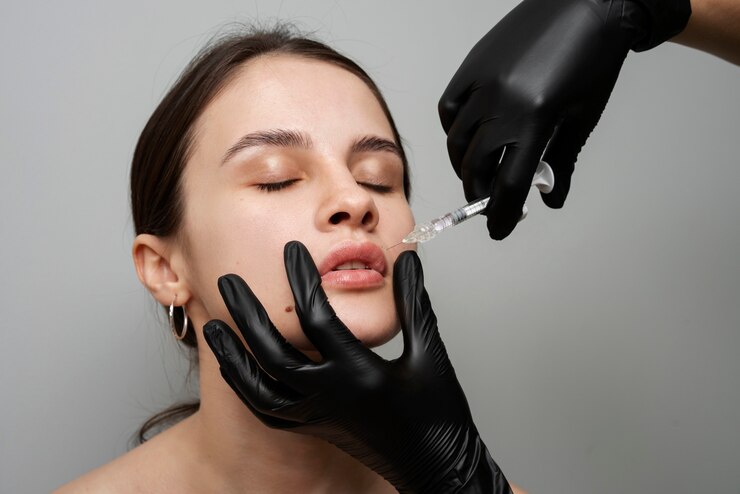

- Duration:
90 min.
- Start at:
$250
- FAQ:

- Precare:

- BOOK A CONSULTATION
Botox
Botox, short for botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Despite its origins in a potentially harmful bacterium, Botox has found widespread use in the field of cosmetic and medical procedures. In cosmetic applications, Botox is renowned for its ability to temporarily reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles and fine lines by paralyzing the underlying muscles.
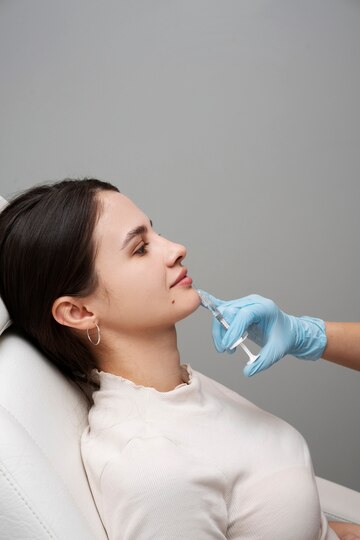
It achieves this by blocking nerve signals in the targeted muscles, resulting in a smoother and more youthful complexion. Apart from its cosmetic applications, Botox has proven valuable in various medical treatments. It is commonly used to alleviate conditions such as chronic migraines, muscle spasms, and excessive sweating. The neurotoxin works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction, thereby providing relief from conditions associated with overactive muscle activity.
The administration of Botox is typically performed through injections, and its effects are temporary, lasting for several months before requiring a repeat procedure. While Botox has garnered popularity for its cosmetic benefits, it remains a subject of ongoing research and development for its potential applications in treating a range of medical conditions. As with any medical or cosmetic procedure, individuals considering Botox treatments should consult with qualified healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective use.
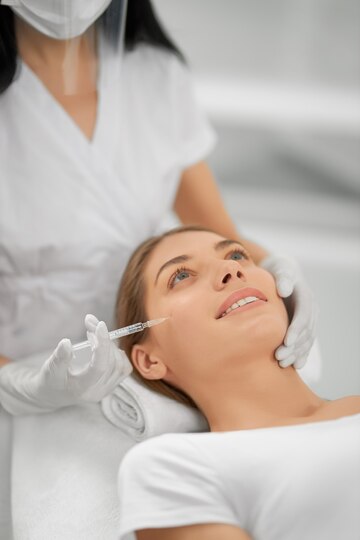
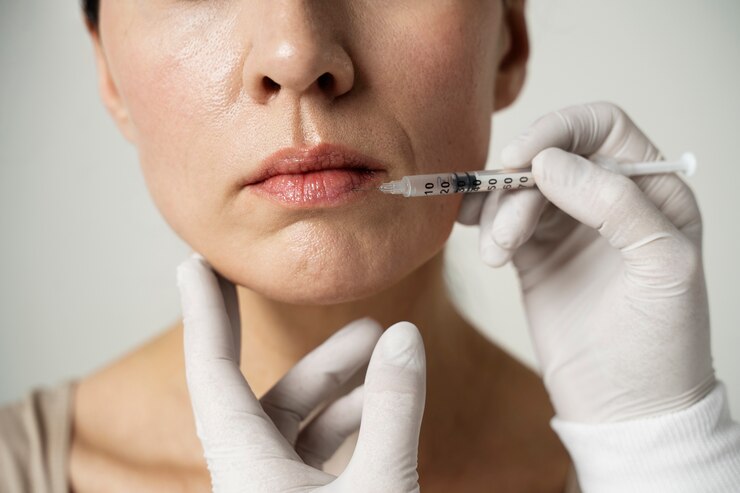
Our Goal & Results
Botox, short for Botulinum Toxin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. While it is a deadly toxin in its natural state, when used in medical and cosmetic applications, it is purified and diluted to create a safe and effective treatment. Goal of using Botox in medical and cosmetic settings is to temporarily paralyze or weaken muscles. This is achieved by blocking nerve signals in the muscles where it is injected.
The results of Botox treatment are temporary and typically last for several months. The specific duration can vary from person to person. The effects of Botox injections become noticeable within a few days to a week after treatment.
Precare Tips
- Provide a comprehensive medical history, including any medications, supplements, or allergies, to ensure there are no contraindications or potential complications.
- Discuss realistic expectations for the results of the Botox treatment and understand that individual responses may vary.
- Maintain good hydration by drinking an adequate amount of water in the days before the procedure, as this can contribute to overall skin health.
- Clearly communicate with the healthcare professional about the specific areas you want to address and the desired outcome.
- Consider using arnica or other recommended topical treatments before and after the procedure to help minimize bruising.
- Inform the healthcare professional if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant, as the safety of Botox during these conditions may need further discussion.
- Be vigilant for any unusual or severe reactions and promptly report them to the healthcare professional.
FAQs
Botox is a cosmetic treatment that involves the injection of botulinum toxin to temporarily paralyze muscle activity. It works by blocking nerve signals in the muscles where it is injected, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Botox is commonly used for cosmetic purposes to smooth wrinkles and lines on the face, particularly in the forehead, around the eyes (crow's feet), and between the eyebrows. It is also used for medical conditions such as chronic migraines, excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), and muscle spasms.
The effects of Botox are temporary and typically last between three to six months. After this period, muscle activity gradually returns, and wrinkles may reappear. Regular maintenance treatments are often recommended to sustain the desired results.
While Botox is generally considered safe when administered by qualified professionals, there can be side effects such as temporary bruising, swelling, or redness at the injection site. In rare cases, individuals may experience headaches, muscle weakness, or allergic reactions. It is crucial to consult with a licensed practitioner to minimize risks.
Botox is generally suitable for adults who are in good overall health and wish to address wrinkles or certain medical conditions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with certain neurological disorders, and those with allergies to botulinum toxin should avoid Botox. A consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine if Botox is a suitable option based on an individual's medical history.
